Ways4eu WordPress.com Blog
SPA View of ways4eu.wordpress.com
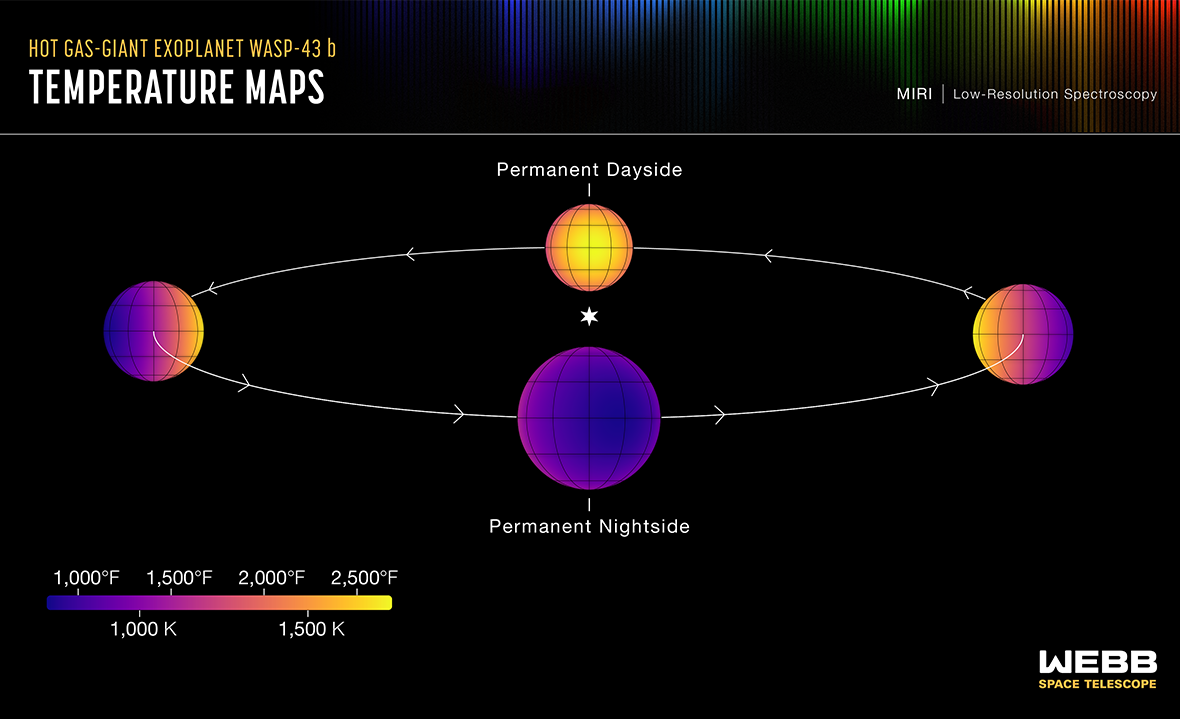
Temperatures on Exoplanet WASP 43b
By iftttauthorways4eu
on Fri May 03 2024
A mere 280 light-years from Earth, tidally locked, Jupiter-sized exoplanet WASP-43b orbits its parent star once every 0.8 Earth days. That puts it about 2 million kilometers (less than 1/25th the orbital distance of Mercury) from a small, cool sun. Still, on a dayside always facing its parent star, temperatures approach a torrid 2,500 degrees F as measured at infrared wavelengths by the MIRI instrument on board the James Webb Space Telescope. In this illustration of the hot exoplanet’s orbit, Webb measurements also show nightside temperatures remain above 1,000 degrees F. That suggests that strong equatorial winds circulate the dayside atmospheric gases to the nightside before they can completely cool off. Exoplanet WASP-43b is now formally known as Astrolábos, and its K-type parent star has been christened Gnomon. Webb’s infrared spectra indicate water vapor is present on the nightside as well as the dayside of the planet, providing information about cloud cover on Astrolábos. via NASA https://ift.tt/hytMLNS